Important Notice
If you are a doctor, dietitian, nurse, pharmacist, then click on I’m a healthcare professional to proceed. For persons other than Health care professionals, we request you to visit www.danone.in.
By - Danone Nutricia academy

The gut microbiome is a crucial determinant of human health by promoting its maintenance.For instance, it aids in the immune responses, and helps synthesize vitamins.1 The gut microbiota composition is influenced by long-term diet. Nutritional components such as carbohydrates, energy, protein, fat, prebiotics and fibers modulate the gut microbiota composition in adulthood.2 For instance, consumption of prebiotics by children promote the bifidobacterial populations, increase calcium absorption, and may exert long-term health benefits.3 Thus, establishing the roles of dietary components in gut microbiota composition, especially from early life, is vital for early nutritional interventions.2
This Journal Watch discusses how dietary components modulate the gut microbiota composition. The study reviewed examined the gut microbiota composition and their correlation with long-term dietary intake from infancy to late adolescence-published in the Journal of the Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics.
Study 1: Gut Microbiota Composition in Children with Different Dietary Habits
The study goal was to correlate dietary consumption with microbiome features in a diverse population of children.
Table 1 shows the design of the study.
Table 1. Study design to assess the correlation between gut microbial composition and dietary patterns in children.Adapted from: Herman et al. 20191
| Study type | Cross-sectional study |
| Participants and dietary patterns |
Healthy children between 2 to 9 years of age
Food groups:
|
| Inclusion criteria |
|
| Exclusion criteria |
Healthy children between 2 to 9 years of age
Children who:
|
| Outcome measures |
|
For α-diversity:
For β-diversity:
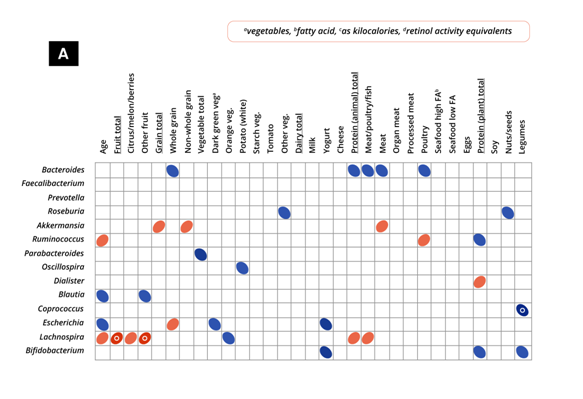
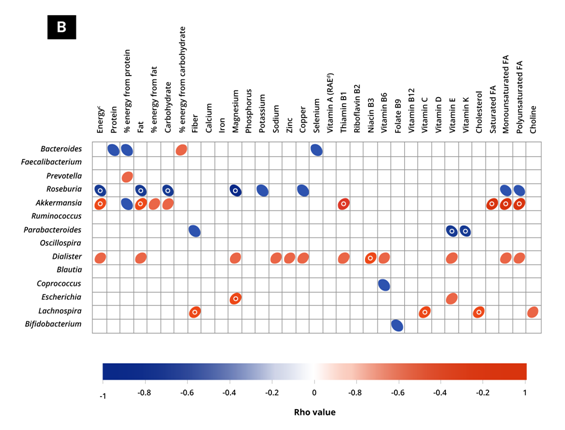
Figure 1. Different bacterial genera, their relative abundance, and their correlation with (A) several food groups consumption and (B) nutrient intake in children between 2 to 9 years of age. Adapted from: Herman et al., 2019.
Ellipses show correlations only with uncorrected P<0.05. ‘o’indicates significance post false discovery rate correction (P≤0.05). Each ellipse width is proportional to the correlation strength (i.e., Spearman values)
Dietary macro-and micronutrients influence the overall gut microbiota composition throughout early life. As children grow, the gut microbiota matures and gets more diverse, suggesting that assembly of the gut microbiome starts fromearly childhood. A few key dietary components, such as foods high in fibers, vitamins, and minerals, by consuming diverse plant proteins have the strongest associations to gut microbiota development.Prebiotics consumption by children promote the bifidobacterial populations, yielding long-term health benefits. In conclusion, dietary choices and patterns at an early age stronglyinfluence the gut microbiota in the long run. Therefore, early interventions with the right nutrients will improve gut- and overall health.
For the use of healthcare professionals only, not for distribution to general public.
CVM code: 1650889856318